The WS2812 is a popular type of LED widely used in DIY electronics and lighting projects due to its simple control method and capability for full-color illumination. Each WS2812 unit consists of a red, green, and blue LED (RGB) and an integrated control circuit, all packaged into a single component. This integrated control circuit allows each LED to be individually addressable and controlled using a single data line, making them very efficient in terms of wiring and control complexity. Here’s a detailed look at the WS2812 protocol:
1. Communication Protocol
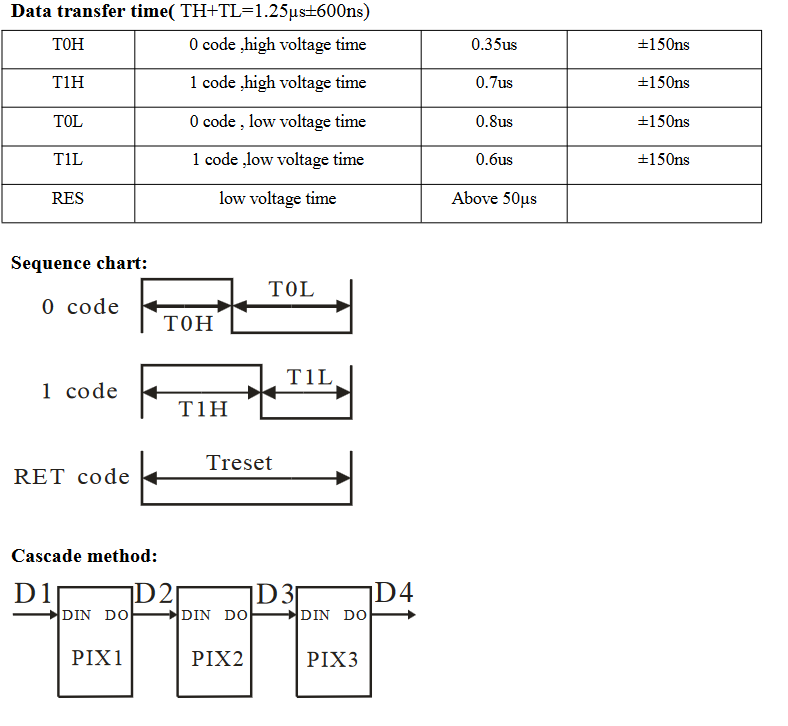
The WS2812 LEDs are controlled through a serial communication protocol that uses a single data line. This protocol is timing-specific, where the duration of the signal high and low times determines whether a bit is interpreted as a ‚0‘ or a ‚1‘.
2. Data Format
Each WS2812 LED receives its color brightness data in a series of 24 bits—8 bits each for red, green, and blue color components. The order in which these color bits are sent can vary by manufacturer but is typically green, red, and then blue. The data for each color is usually sent as follows:
- Green: 8 bits
- Red: 8 bits
- Blue: 8 bits
3. Timing Requirements
The WS2812 protocol is very timing-sensitive. The data is sent using pulses of specific durations:
- 0 bit: A short high pulse (about 400 ns) followed by a longer low pulse (about 850 ns).
- 1 bit: A long high pulse (about 800 ns) followed by a short low pulse (about 450 ns).
The exact timing can vary slightly between different batches of LEDs or different manufacturers.
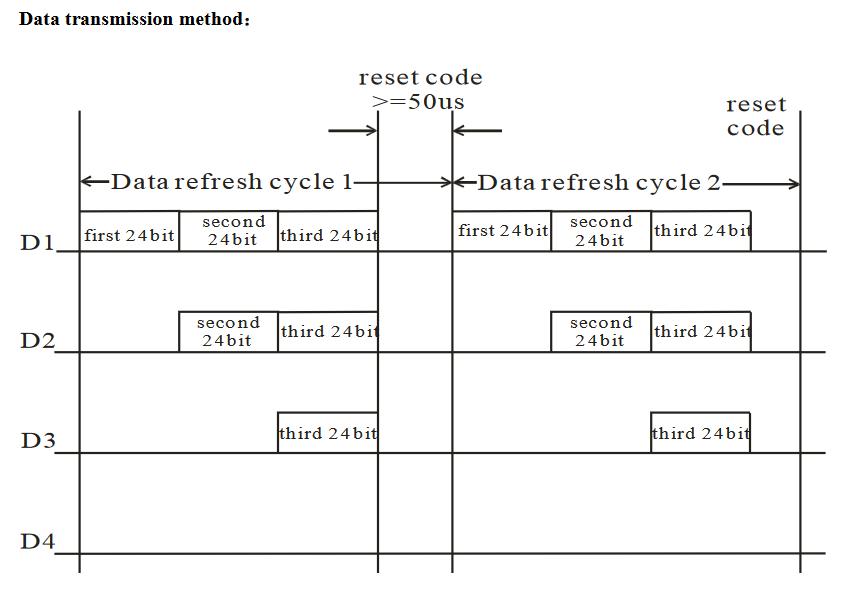
4. Reset Pulse
At the end of a sequence of LED data transmissions, a reset pulse is sent to tell the LEDs to update their displayed color based on the data they received. This reset pulse is a low signal that must last at least 50 microseconds.
5. Cascading LEDs
Multiple WS2812 LEDs can be chained together. Data is sent in a stream from the microcontroller to the first LED in the chain. Each LED extracts its 24-bit portion and passes the remaining bits down the line to the next LED. This cascading feature allows complex displays to be built using hundreds of LEDs while still requiring only one data line from the controller.
6. Power Requirements
Each WS2812 LED typically operates at a voltage of about 5V. The current draw can be significant when many LEDs are used, especially if all LEDs display white at full brightness, as each LED can draw up to about 60 mA.
Attachements: